As big data and cloud computing have become more popular, the market for cloud analytics has taken off. In the February 2017 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Business Intelligence and Analytics Platforms report, a majority of those surveyed (51 percent) said that they had active or planned cloud business intelligence (BI) deployments. Gartner analysts added, “We expect this trend to continue, with the majority of new license buying (more than half) likely to be for cloud deployments by 2020.” Overall, the firm forecasts that the BI and analytics market will grow 7.9 per year through 2020.
A Harvard Business Review report commissioned by Oracle found even higher interest in cloud analytics: 69 percent of those surveyed expected to be using cloud analytics by the end of 2017.
Protecting your company’s data is critical. Cloud storage with automated backup is scalable, flexible and provides peace of mind. Cobalt Iron’s enterprise-grade backup and recovery solution is known for its hands-free automation and reliability, at a lower cost. Cloud backup that just works.
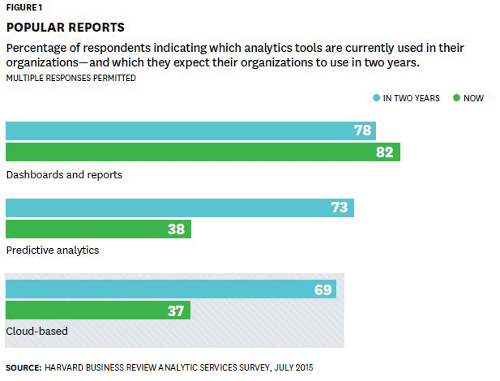
Source: the HBR report cited above.
This article will cover the definition of cloud analytics, the benefits of cloud analytics, cloud analytics challenges, popular use cases and links to popular cloud analytics tools. For help choosing a cloud provider for your business, see our comprehensive guide to cloud computing.
When people use the term “cloud analytics,” they are usually talking about big data analytics software that is delivered on a software as a service (SaaS) basis. According to Gartner, “Analytics has emerged as a catch-all term for a variety of different business intelligence (BI)- and application-related initiatives. . . . Increasingly, ‘analytics’ is used to describe statistical and mathematical data analysis that clusters, segments, scores and predicts what scenarios are most likely to happen.” Other terms used to describe the same software include cloud-based BI, SaaS BI or SaaS analytics.
Sometimes, however, people use the term “cloud analytics” to refer to analysis of data related to cloud computing. These are usually cloud management solutions that monitor the performance of cloud infrastructure and applications.
This article will focus primarily on the first definition of cloud analytics (big data analytics delivered through the cloud) rather than the second (analysis of cloud-related data).
Cloud analytics brings together the benefits of cloud computing and the benefits of big data analytics. Some of the most important benefits of cloud analytics include the following:
A 2016 Aberdeen Group report found that many of these benefits are greater for organizations using cloud analytics than for those using on-premise BI solutions. The cloud advantage was particularly strong when it came to business user satisfaction with their analytics tools, customer retention and revenue growth.
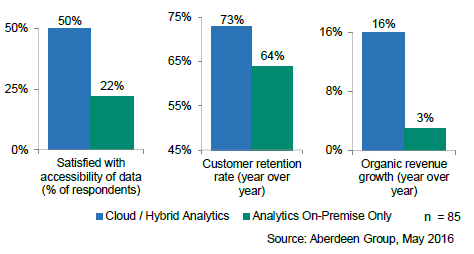
While cloud analytics offers a number of significant benefits, enterprises will also face some challenges with their cloud analytics efforts. Some of the most significant potential pitfalls include the following:
Organizations apply cloud analytics capabilities to a wide variety of different domains. For example, business users might analyze sales, marketing, supply chain or customer service data to look for new opportunities. They might analyze transaction data to look for fraud. Frequently, they also incorporate external data, such as customer demographics, market size and competitive information, into their analysis in order to improve their marketing and forecasting capabilities.
The IT team can also make use of cloud analytics. For instance, they might use cloud-based tools to analyze their Web traffic, to spot security incidents in log data or to track the performance of their cloud-based infrastructure and applications.
Some vendors sell customized cloud analytics tools that are tailored to one of these specific needs, such as sales or marketing. Others sell tools with more broad capabilities that can be adapted to different use cases.
Cloud analytics vendors fall into two broad categories: those who only offer analytics tools and those who offer a wide variety of enterprise software, including cloud analytics. Some of the better-known cloud analytics tools from both categories are listed below, in alphabetical order:

Datamation is the leading industry resource for B2B data professionals and technology buyers. Datamation's focus is on providing insight into the latest trends and innovation in AI, data security, big data, and more, along with in-depth product recommendations and comparisons. More than 1.7M users gain insight and guidance from Datamation every year.
Advertise with TechnologyAdvice on Datamation and our other data and technology-focused platforms.
Advertise with Us
Property of TechnologyAdvice.
© 2025 TechnologyAdvice. All Rights Reserved
Advertiser Disclosure: Some of the products that appear on this
site are from companies from which TechnologyAdvice receives
compensation. This compensation may impact how and where products
appear on this site including, for example, the order in which
they appear. TechnologyAdvice does not include all companies
or all types of products available in the marketplace.